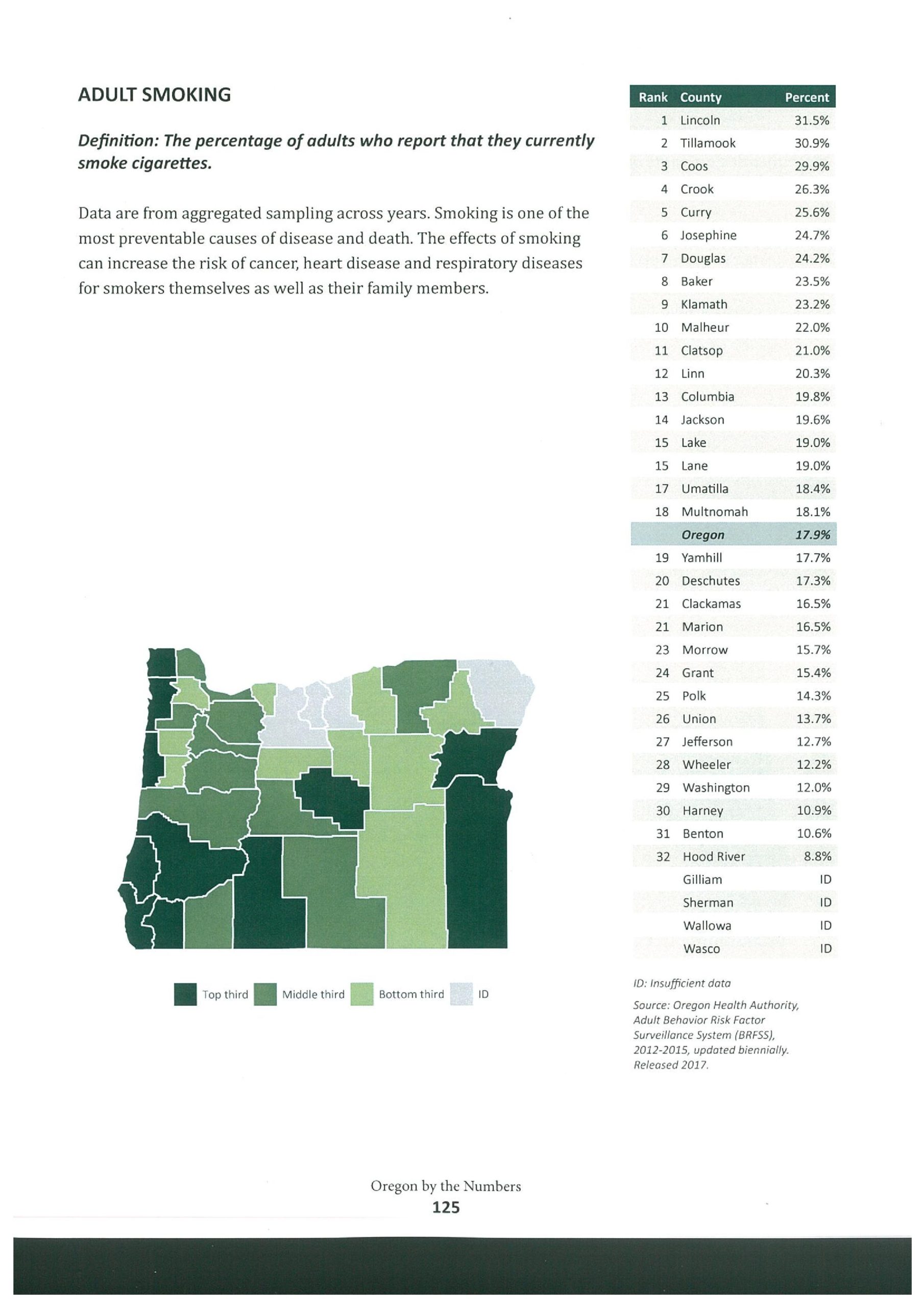
We’re #2! Sometimes being near the top is not a good thing. The percentage of adults who smoke in Tillamook County is second highest among all Oregon counties. Recent data shows the percentage of people who smoke statewide is 17.9%. By comparison, the percentage in Tillamook County is a whopping 30.9%.
There is some good news. Smoking rates have been declining over the past several decades. It is a known fact that smoking poses serious health risks, negatively impacting vital organs like the lungs and the heart.2 But did you know that smoking can increase your risk for Type 2 diabetes?2
Tillamook County Wellness is committed to increasing awareness about the risk factors for developing Type 2 Diabetes, with a goal of inspiring and motivating citizens to take steps toward improved health behaviors. The following information from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) explains how tobacco use increases risk for developing Type 2 Diabetes and how smoking worsens the condition for those who already have it.
Smoking cessation is covered by insurance. Ask your medical provider for information about the best options and support for quitting smoking and to reduce your overall risk for Type 2 Diabetes through changes to your lifestyle.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a disease in which the body’s blood sugar levels are abnormally elevated. When digested, carbohydrates from food are turned into a natural sugar called glucose, which is used by the body’s cells for energy. Glucose is ushered into the cells by a hormone called insulin. People with diabetes are unable to make or efficiently use insulin, causing glucose to build up in the blood without making its way to the cells.3
There are two types of diabetes. The most common of these is Type 2, or adult-onset diabetes, which accounts for more than 90% of all diabetes cases3 and is the seventh leading cause of death in the United States.1 Research has found that smoking is a direct cause of Type 2 diabetes. In fact, smokers are 30-40% more likely to develop Type 2 diabetes than nonsmokers, and smoking is responsible for about 9,000 diabetes deaths in the U.S. per year.2
How Does Smoking Affect Diabetes Management?
Diabetes is a serious yet manageable health condition, but smoking can worsen the disease, causing additional problems.4 Smokers with diabetes are more likely to have trouble regulating their blood sugar levels with treatment than diabetic nonsmokers.1 Diabetics who smoke are also at a higher risk for disease complications than nonsmokers with diabetes, including: 1,3
- Poor blood circulation in the legs and feet that can lead to infections, ulcers, and even amputation of toes and feet
- Heart disease
- Kidney disease
- Retinopathy (an eye disease which can lead to blindness)
- Nerve damage in the arms and legs that can cause numbness, pain, weakness, and poor mobility
How Can You Lower Your Risk for Type 2 Diabetes?
- Don’t start smoking. Smoking increases your chance of having Type 2 diabetes.4
- If you smoke, lower your risk for Type 2 diabetes by quitting. Find a quitting method that works for you.
- USDHHS Consumer Booklet 2014 – U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (USDHHS). Let’s Make the Next Generation Tobacco-Free: Your Guide to the 50th Anniversary Surgeon General’s Report on Smoking and Health (Consumer Booklet). Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health; 2014.
USDHHS 2014 – U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (USDHHS). The Health Consequences of Smoking—50 Years of Progress: A Report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health; 2014.
3. CDC 2015 – Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (CDC). Smoking and Diabetes. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health; 2015. http://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/campaign/tips/diseases/diabetes.html#two. Accessed January 6, 2016.
4. NIDDK 2014 National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Prevent Diabetes Problems. Bethesda, MD: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2014. http://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-topics/Diabetes/prevent-diabetes-problems/Pages/index.aspx. Accessed January 6, 2016.
https://www.fda.gov/TobaccoProducts/PublicHealthEducation/HealthInformation/ucm490916.htm